frigidarium (cold room)
tepidarium (warm room)
caldarium (hot room) with a hot plunge bath
apotyderium (changing room)
cold plunge bath
soakroom

Wall paintings of marine scenes from the new bath suite.

Explore the map and Click on the Mosaic to find out more!
 |
| Ligulae - cup shaped scoops that can be used for removing earwax, aplying makeup or ointments and as a medical instrument. Spatulae - a small spatula that can be used as a medical instrument or craft tool. |
 |
| Manicure set of tweezers and nail cleaners. |
Bathing was an important part of Roman life. Roman baths were used not only for keeping clean and healthy but were also often major venues for socialising and business negotiations, rather like the equivalent of the golf course.
Public bath houses were available to both the rich and poor - although the rich often also had their own bath suites such as the ones at the first Bancroft Villa and the final Grand Villa.
Roman baths contain a series of rooms and baths which the bather moves through from cold to hot and then in the reverse. They work like modern Turkish baths aiming to induce a sweat. Oil is then applied to the skin, which is then scraped off with the dirt and body toxins using an instrument called a strigil.
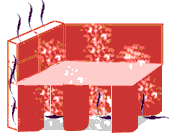
Floor and wall heating
A furnace in the stokeroom provides both hot water for the baths and heat for the rooms. The walls are heated by air circulating through hollow tiles. The floor is raised on tiled columns that allows hot air to circulate under and heat the floor. This type of heating is called a hypocaust system and permitted Romans to have a central heating system.